Products & Services
Recombinant Proteins
FGF Family And Receptors
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) regulate various developmental and metabolic processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, wound healing, nerve regeneration, chronic inflammation, and cancer growth. The FGF family consists of 22 members that share the β-trefoil fold despite their relatively low sequence identities (13–71%). The β-trefoil fold contains 12 β-strands that form 6 two-stranded β-hairpins (i.e., β1-β12, β2-β3, β4-β5, β6-β7, β8-β9, and β10-β11). Hairpins are arranged in a pseudo three-fold symmetry: the first, third, and fifth β-hairpins form a barrel that is covered by a triangular cap consisting of the second, fourth, and sixth β-hairpins.
FGFs are divided into FGF1, FGF4, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9, FGF11, and FGF19 subfamilies depending on their sequence similarities. Except for the intracellular FGF11 subfamily, FGFs form complexes with FGF receptors (FGFRs) on the cell membrane, which are generally composed of three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like extracellular domains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. FGFs bind to the interface between the second and third Ig-like ectodomains to induce receptor dimerization, leading to the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain to stimulate signaling pathways.
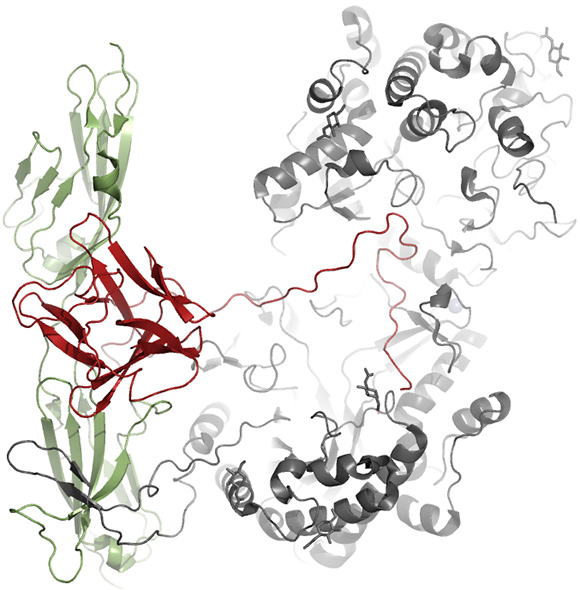
The canonical FGFs (FGF1, FGF4, FGF7, FGF8, and FGF9 subfamilies) have a positively charged sector clustered by lysine and arginine residues and thus display avidity for negatively charged heparin/heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) present on the cell surface or in the extracellular matrix. Therefore, canonical FGFs form ternary complexes with HSPG and FGFR, and act in the vicinity of cells as paracrine and/or autocrine factors. Conversely, FGF19 subfamily members (FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23) have no apparent HSPG-binding site on their surfaces and thus perform their physiological roles in an endocrine manner. They are released from the extracellular matrix and reach
Complex model structure of
FGFR1c/FGF21/KLB